Introduction
‘The only weirdness about the quantum world is our insistence that it is a consequence of size, and not time.’
The Thread
We’re all generally comfortable with time having a notion of past, present and future. And we’re also happy to accept, even if we find it somewhat weird, that time and space have been proven to be interdependent features of a unified spacetime. However, despite this there seems to be a lack of corresponding notion of past, present and future applied to space. To do so is hard to begin with. But like a magic eye picture, once you’ve seen it, it’s hard to unsee it. This view is a central thread on which this Molimentum approach pulls.
Grounded in Fact
Take the example of the question ‘What time is it on the moon now?’ Carlo Rovelli has explained this question makes no sense as time is relative to different positions. What we’re exploring is an extension to this idea that proposes that it is not just the distance that creates the obstacle to answering the question but the scale of the observer (you) relative to the object (the moon). Further, we consider how we may glean valuable insights by quantifying by just how much we may not synchronise objects and observers and how much this is owing to these two different factors.
The Cat Is Alive
In terms of thought experiment, the Molimental approach argues that Schrodinger’s Cat is alive and that the experiment is only capable at best of proving whether the cat will die or will not. Extrapolating what is happening ‘now’ for the cat (a bigger object) based on the events ‘now’ of a smaller object is not reasonable for the same reason we can’t tell what time it is on the moon now, but specifically owing to scaly nowness rather than linear nowness.
The problem here has always been in the question, not the answer. This approach suggests that the weakness in the experiment is to conflate the now for two objects of different scales, even if one is inside the other. As a thought experiment this remains a purely scale based issue, so may be addressed without implications of observation..
Testing, Testing
Admittedly, there is complexity in determining what to consider the scope of the observed object scope of the observer. Is it the person/optical system/eyeball/receptor/cell/atom? However by using a common approach to both observer and object it is assumed to be likely to allow consistency and possible to test this theory experimentally. The testing would also rely on the ability to create large objects that could be limited to act like smaller objects in order that the scale is isolated from the size of the object’s fundamental atomic structure.
Measuring Nowness
The distance between an object and observer denies the synchronicity required for a simultaneous measurement. Molimentum Theory considers this lack of synchronicity as a ‘linear’ question of nowness. It can be measured, compared to other distances.
The further addition to this picture is to consider scale as another means by which the synchronicity between locations. The relative scales offer a different barrier to synchronicity which may be considered ‘scaly’ nowness’. Significantly, both may also be measured.
The hypothesis being proposed is that when the scale of the observer is smaller than the observed object the observer witnesses the ‘space-past’. Observing a smaller than observer object, the observer may see the ‘space-future’.
Space-Past and Space-Future, Anyone?
The theory proposes that the relatively small may be considered a ‘space-future’ and the relatively large may be considered a ‘space-past’. We might be used to factoring distance into observations. However the relative scale of observers and objects is generally omitted from consideration. It’s something the Molimental approach suggests comes at a significant cost to our understanding of the physical world.
‘The future is uncertain. Uncertainty increases at smaller scales. To be smaller is to be quantum.Quantum is future. ’
Quantum rules only apply for the very smallest things. At this micro-scale, nature is entangled, interdependent, quantised, probabilistic, and uncertain. Think again, how might you describe what the future might reasonably look like? While intuition is unpopular with proper scientists, isn’t it reasonably and intuitively entangled, interdependent, quantised, probabilistic, and uncertain.
Making Sense of Young
In terms of a physical experiment we can apply this approach to Young’s Double Slit Experiment. As a physical experiment it requires that we add a layer to the thought experiment, that of how observation plays a part.
In this experiment the atoms of our eyes are of similar proportion to the atoms being observed. On the cusp of both smaller on larger, we are permitted an ability to flick between classical and quantum views, like spacetime bifocals. Young’s experiment flips between observing the future (a place in which uncertainty reigns and in which waves are observed) and the past (a place in which uncertainty is invalid and particles are observed).
The future does not feature duality, nor does the past. That is only available in the present.
For this experiment we need to consider what distinguishes the future from the past. A central feature of the future is its uncertainty. In this realm of ‘maybe’ the core units are limited to probabilities. The past is distinguished in that there are certainties, so not the realm of possibilities but of certainties, with the core units being a binary yes and no. The present is simply where we may have one foot in the future and one in the past. It’s an experience more than a place in spacetime.
Individual particles sent in sequence, one after the other may appear to be interacting because we are witnessing a ‘space-future’. If the experiment is set up with single or observed slits where the set up invalidates a ‘maybe’ result and limits them to a binary yes/no response, creating a space-past view in which particles are seen. If the experiment is set up to create probabilistic outcomes we see the wave like interactions.
The set up of experimental scenarios will dictate prevailing results observed, based on whether they allow uncertainty (small, future) or not (big, past). Young’s experiment allows inherently space-futuristic objects (owing to their relatively small size) to be observed with a space-future perspective (in which uncertainty and therefore the future is included), and also but separately, with a space-past perspective (in which classical, binary outcomes are possible).
In the experiment, the baffling outcomes are most often attribute to the matter of observation. More accurately, the significant aspect of the observation is not any anthropomorphic matter of humanity or consciousness but the observation’s feature of sharing a common moment or synchronicity between two objects, in unified spacetime.
Punchlines
In summary, by equating the relatively small as a form of relative future we can unlock the confusion surrounding unifying the quantum and classical observations of the world.
In unfurling this work further, the main headlines are that the Molimetum process is Gravity. Dark Matter is macro-Gravity-past. Dark Energy is micro-Gravity-future’. Spacetime is emergent from the Molimentum process. Molimentum is Gravity. NB, I’m giving Gravity a capital letter to indicate its elevated importance as understood according to Molimentum Theory.
The quantum forces of electro-magnetism, weak radiation and strong radiation are linear forces recurring along the generational flow of the Molimentum process and matter is the effect of lateral, perpendicular to the the flow of the process.
Further notes shared here will expand on these claims.
The Aims
‘The only reason to find the quantum world mysterious is if you insist its weirdness is a matter of scale alone and choose to ignore the impact that the relative scales of object and observer have on time.’
STIMULATING INSIGHTS
The aim of this work is to share insights. This work aims to prod, poke and provoke thinking and productive new perspectives. In particular, new perspectives and ideas to test links between quantum and classical world perceptions.
NECESSITIES OF SCOPE
In order to unite gravity with the quantum satisfactorily, the approach explored here considers it necessary to unite perception and consciousness too. These four features are considered as interdependent aspects and derivatives of one single process which is labelled ‘Molimentum’.
MULTIPLE ENTRY POINTS
You can attack this book by taking any of the chapters first. If you get bogged down with any of the chapters, trying another one may prove more fruitful. Especially the one on Molimentum Theory itself, you might want to come back to that one after exploring the challenges to which it is set.

FIG. 1 - Molimentum Theory requires an interdependence of these 4 things.
The Chapters
0. Molimentum
- Origins – Where did this idea emerge from?
- Context – On which assumptions has it been shaped.
- Features – What does this Molimentum look like?
1.Structure
- Time – Merging smooth and quantised time.
- Spacetime – Grasping the impact of scale on time.
- Normal/Darkness – The pushing and pulling of the Universe.
2. Contents
- Forces – ‘Linear’ imbalances along generational lines.
- Matter – ‘Lateral’ imbalances across generational lines.
- Related Theories – As understood through Molimentum.
3.Observation
- Nowness – The importance of asynchronicity.
- Duality – A defining symptom of the present.
- Relevant Experiments – As understood by Molimentum.
4.Consciousness
- Thinking – Questions as answers.
- Actions – A semi-physical approach to the hard problem.
- Subconscious – Clues of the unknown knowns.
5.Conclusion
- Summary – Molimentum in a nutshell.
- Testing – How this view may be tested.
- Unknowns – Areas yet to be assessed in terms of Molimentum.
0.1 Origins
Where did this idea come from?
Around 2003 I worked as a kindergarten teacher in Shenzhen, China. I had taken a copy of Hawking’s Brief History of Time with me and a sense that it’s something we all ought to read at some point. As I read it I found myself adding notes, arguing in the margins.
I began to relate the physics I was reading with learnings from another book I had taken ‘Story: Substance, Style, Structure and Principles of Screenwriting’ by Robert McKee. The central point I took from this were the ingredients in a story being a dynamic flow of yes, no and maybe as a protagonist and story seek a satisfying conclusion.
This work is basically what happens when I applied the principles of screenwriting to physics. The name Molimentum came from a boat which my dad fitted out for 3 years in our yard at home. He chose it for three reasons. Firstly, its latin meaning ‘A great endeavor’. Secondly because the Moli part of it aligning with the common practice of giving boats female names. Thirdly because the model of boat (an Ebbtide 36) is chunky and made from steel lends itself to a sense of momentum implied by the -mentum part of the name.
For me, the emerging quest exploring the boundaries of physics has felt like a voyage, the Universe feels feminine in the same way we consider ‘mother nature’ and both the exploration and the resulting theory have a sense of momentum.
For five years I developed my hobby further as a novel I wrote called ‘Shooting Curves’. It was quite mad, as I was at the time, being in a period of active alcoholism. Perhaps it required a little madness to latch on to the concepts I developed, but to give other a chance to join in the thinking requires sobriety, so I’m rewriting up the theory without this time wrapping it up in a stream of consciousness thriller about a nude photographer!
0.2 Context
What foundations of understanding are this work built on?
Over subsequent years I have dipped into some more accessible, popular science books on the subject of how we struggle to reconcile the quantum and classical worlds we perceive. I have particularly enjoyed the writing of Lee Smolin. In particular I like the clarity with which he identifies the principles that unification theories will need to meet in order to prove meaningful. There are outstanding gaps and overlaps in existing understanding, some identified by Smolin, which expose the boundaries and therefore the context or current understanding. My understanding of these are as follows:
The Background Independence Problem
A unification theory must include a description of its own background conditions, as well as the ‘foreground’ things. Significantly, for example quantum mechanics exists within smooth, pre-existing time and space whereas gravity automatically factors in spacetime.
The Discontinuous Time Problem
Potentially overlapping with the background problem, unification requires a method by which to connect smooth spacetime as matches with relativity with the quantum world of discrete units of spacetime.
The Proportional Distribution Problem
Unification theories must shed light on the proportions of matter, energy and theoretical constants evident to us.
This work is developed with these principles in mind. These are the benefits that ought to be derived from a meaningful unification theory.
0.3 Features
So what does this ‘Molimentum’ theory look like?
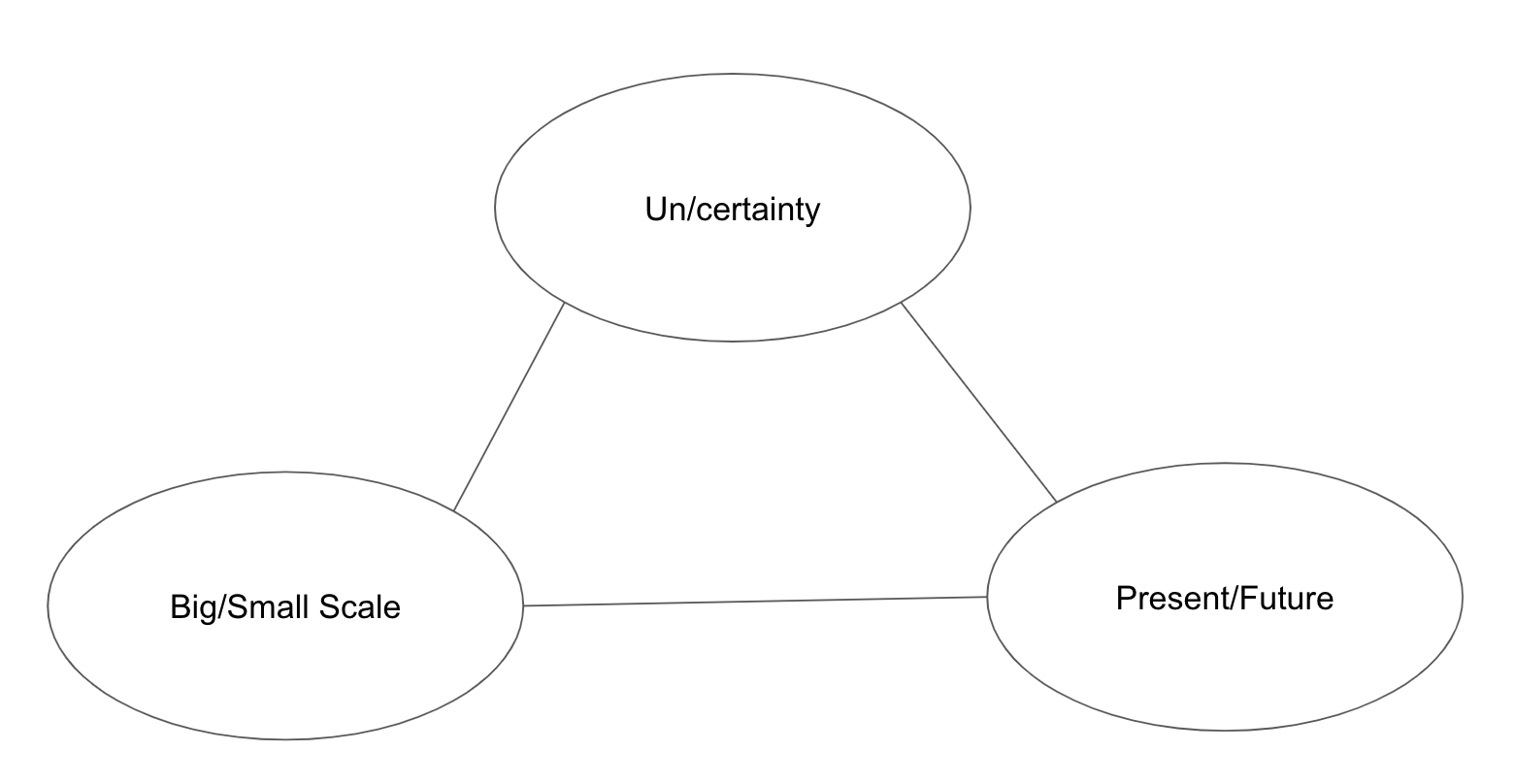
Fig 2.
The process that is referred to here as Molimentum is presented as the building blocks of the meta Universe, and could reasonably inform the development of the physical Universe.
In this process the concept of Yes, No and Maybe are conceptual ingredients of this process. These elements were plucked from Robert McKee’s non-fiction book on screeenwriting
Y -> N -> M
N -> Y -> M
M -> Y + N
The Molimentum process is at its heart the manifestation of two kinds of opposite, one polar opposite and one abstract opposite. E.g. The polar opposite of 1 apple is minus 1 apple, similar to yes being the opposite of no. The abstract opposite of 1 apple is everything that is not one apple, similar to the relationship between yes and maybe, and between no and maybe.
Taking any one of these concepts demands the presence of the others in order for them to have meaning. They are interdependent.

Fig 4.
A spherical view of double opposites (potentially with an open, field like system).
This shows a potential link between the algebraic Molimentum process and its physical 3D geometric aspect.

Fig 7.
A tetrahedron may be considered to represent 4 dimensions of spacetime.

Fig 3.
A spherical view of double opposites (potentially with a closed, particle like system).
A sphere is a physical manifestation of these ‘double opposites’. NB, this illustrates a possible geometry for both particles, and fields.

FIG. 5.
The 3 elements combined at a ‘junction’.
It is considered that there are temporary absences of one or two of these concepts but that a balance between these three concepts is a default to which the metaUniverse is drawn.

Fig. 6.
Separated Elements.
The three items may be understood together as one ‘junction’ and each as three separate ‘paths’.
These four directions align with 4 dimensions of spacetime. This follows the smallest number of points required for a three dimensional space.
The Process
There are 6 fundamental parts, plus a 7th one in the Molimentum process.
Y
N
M
-Y
-N
-M
YNM is the 7th (parts combined together)
At the junctions the unified Yes/No/Maybe is considered to reflect itself and multiply into a further 6 pairs of ingredients as it regenerates.
YNM x -(YNM)
Y-Y, -YY
YM, MY
YN, NY
M-M, -MM
NM, MN
N-N, -NN
The junctions repeatedly split three ways and regenerate, offering a pattern for energy to emulate as it slows. This pattern is dynamic, not static.

Fig 8.
Some paths represent pure paths while others are impure (featuring different patterns of Y, N, M along the way).
Crucially, it is supposed that there is an ‘exhaust like’ energy leftover from the Molimentum process. This can be achieved by a recurring mathematical form. This is a process energy may emulate to becomes normal matter.
Possible Geometry

Fig 9a.
Core elements are related.

Fig 9b.
For the first ‘thing’ the answers to any question about it would be equally both yes and no. These entities split equally as there are no other things to align with. Representation of this third state demands the presence of a third term, which as a blend of yes and no is termed maybe. Taking any one of these terms yes, no and maybe generates the others. In the process shown, each of them evolves as separate and yet also interdependent dimensions.
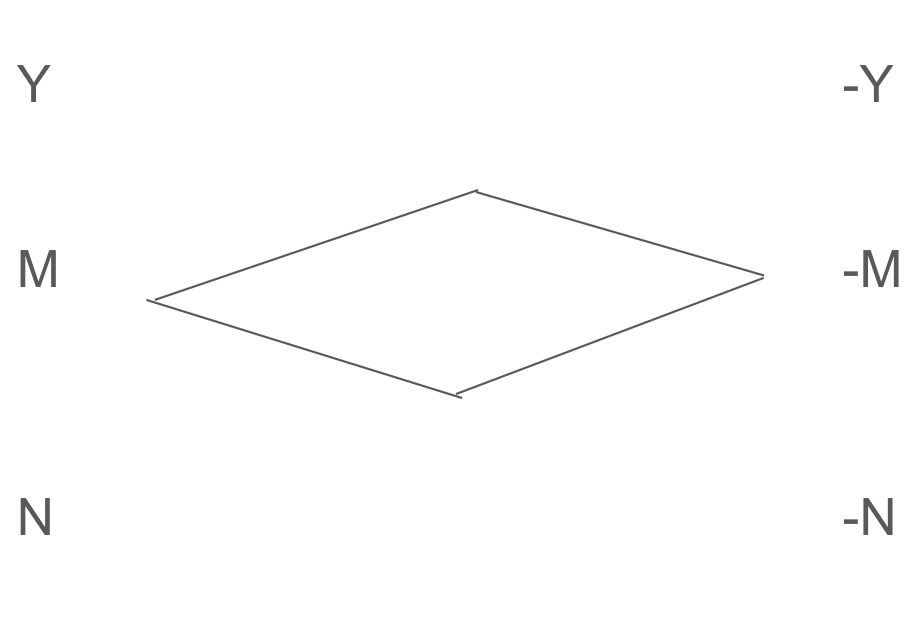
Fig 9c.
Core elements are interconnected.

Fig 9d.
A puff of leftover pure energy emerges into a space created with prior process by which its evolution may be shaped, as its energy decreases.
Whatever the first thing is, at this point it would be possible to state something about it, to which the answer is yes, or no, or at least maybe. However, look at these terms, yes can only mean something with the concept of no, and vice versa.
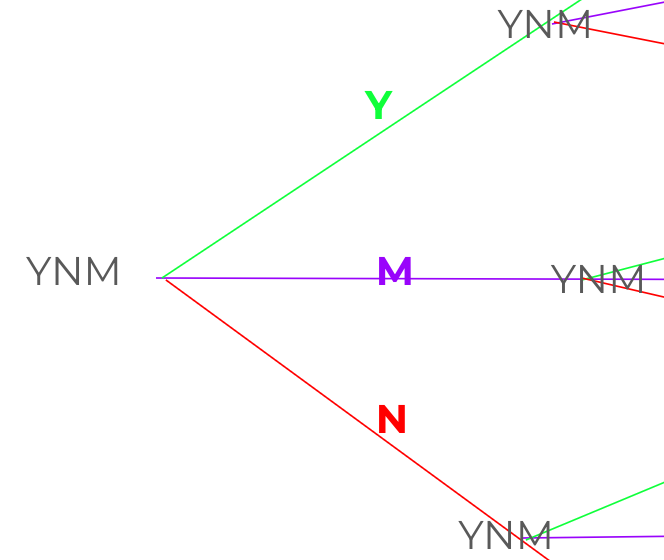
Fig 10.
Core elements interact.
0.4 Molimentum Summary
The proposal is that the Molimentum process is able to provide all the patterns required to create the know features in physics, plus offer insights on unknown aspects. It illustrates maximum complexity from minimal simplicity.
Molimentum Terminology
Since this approach uses a novel metaphysical explanation to shed light of physics it required a new lexicon by which to grasp the new approach more easily.
Trio. YNM when together as a junction.
Inverted Trio. -MNY is the inverse of the Trio.
Core Three. When Y, N, M are separate.
Inverted Core Three. The inverted, minus versions of the core three -Y, -N, -M.
Six Fundamental Pairs. The results from multiplying YNM x -MNY.
Pure Paths. The 3 dimensions along which the Y,N, M axiis recur without change from a singular type.
‘Stop looking at the pitch and watch the game’.
1.1 Time
A significant sticking point in reconciling the quantum world with the classical one is that the quantum only works inside a world of discrete, quantised units while classical physics only works in a world of smooth, pre-exisiting time and space without discrete units. As such, to unite these worlds we need a structure that can offer both of these seemingly contradictory ground conditions.
This diagram shows an example of a process which allows three ‘pure’ dimensions and simultaneously, quantised sections. It shows are sequence of junctions separating three ways and each of which resets as the same kind of junction before separating again, repeatedly.
Three ‘pure dimensions’.

Fig 10.
Illustrating ‘Serial’ Dimensions
1st Generation 2nd Generation (Sequences)

Fig 11.
Note how sequences can be either ‘pure’, or mixed. Over multiple generations the sequence of results can be recurring patterns which can be considered stable, and non-repeating patterns which are not, though whether they repeat (smooth) or not (crunchy) depends on the duration of the sequence observed.
1.2 Spacetime
It is known that time can be easily thought of as having a past, present and future. This view is considered a simplified and incomplete view. As far as I know nobody seems to consider a similar timeline in spacial terms, even though spacetime is accepted as a single entity. This work explores the temporal aspect of scale.

Fig 12.
The idea that when smaller entities observe larger ones they observe a relative, spacial past and when larger entities observe smaller ones they observe a relative, spacial future. The inclusion of the temporal aspect of space is considered a more authentic, full fat picture of spacetime. This issue will be explored further in the Observation/Nowness section.
Unless the observer is the same scale as the observed, there is going to be macro observation of larger objects or micro observation of smaller objects.

Fig 13.
This is illustrated within the Molimentum process, by which the scope opens up wider or reduces. The impact of observing is explored further in the Observation chapter.
1.3 Darkness & Normness
A process that claims to mimic the framework of the universe needs to explain the mysterious properties broadly assigned to dark matter and dark energy.
The evolution of the Universe appears to require a process in which the Universe expands and that also can account for missing mass, in addition to the visible matter observed. The influence is most commonly attributed to Dark Matter and Dark Energy. In terms of Mass-Energy, the ratio of Dark Energy to Dark Matter is approx 3:1 (75% dark energy and 25% dark matter). The Dark Matter brings a kind of anchoring to the Universe while the Dark Energy acts like a spinnaker sail, pulling it onward. This account suggests that Dark Matter and Dark Energy represent elements of gravity, acting across spacetime.
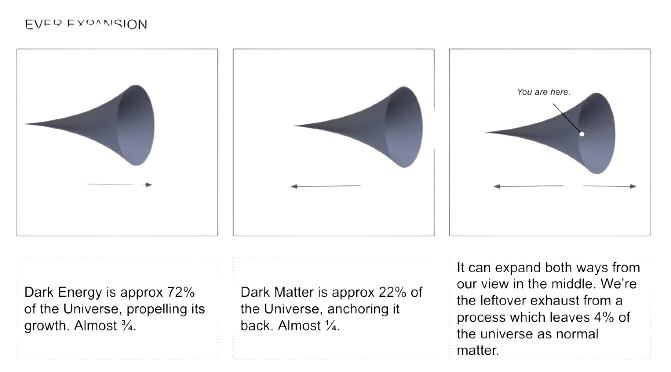
Fig 14.
Above: Repulsive Gravity, Attractive Gravity, Net Gravity.
I speculate that normal matter is a kind of exhaust like leftover from this process repeating. In terms of mass-energy normal matter appears to account for approx 1/20th of total mass-energy.
The normal matter comes from both dark energy and matter, in approx that proportion, so it’s approx 5% Normal Matter, 72% Dark Energy and 23% Dark Matter.
The Molimentum process feature multiplication which pulls the spacetime forward but also division which anchors it.
1.4 Structure Summary
Essentially, this explanation outlines a process that highlights the principles and features required to account for a unified description of the Universe. Namely, emergent spacetime, dark matter and energy, expansion and inflation and a compatible basis for the unification of quantised and classical worlds.
We have seen how patterns, proportions and relations set parametres indicative of the structures on which we hang physics.
Insight: Scientific research seems out of love with the middle. The attention is on going ever smaller and ever bigger but I think the greatest accomplishment is the realm of the fewest phenomena to explain the universe.
‘What we see is not as important as what we don’t see’.
2.1 Forces
Starting with the ‘short’ forces of electro-magnetism, weak radiation and strong radiation, there is an analogous alignment between the combinations of the fundamental states of Yes, No, Maybe. Power of forces appears to derive from the absence of one of the core three parts.

Fig 15.
Electromagnetism. Yes/No, No/Yes.
These opposites mimic the poles found in electricity and magnetism. There is only one way in which this balance may be maintained, as represented by the photon.
Weak Radiation. Maybe/No, No/Maybe.
These terms mimic the defining feature of weak radiation which is a clutch which only permits decay. There are 3 ways in which matter may decay, unlocking previously bound matter, as represented by W-/+ and Zo bosons.
Strong Radiation. Yes/Maybe, Maybe/Yes.
These terms have the opposite clutch effect, which only shows a constructive quality which can be associated with strong radiation which binds atoms together.
There are 8 unique ways in which matter may combine, each represented by the 8 possible gluons.
In respect of strong radiation the r, b, g represent Y, N, M respectively. Notably g is different to the r and b which appear similarly comparable.
Linear Forces
The three quantum forces above all seem to be created by a temporary absence of one of the elements between generations of Molimentum. The absence created a pressure for the third one to be generated. As such it’s possible that the Weak Radiation and Strong Radiation may be the opposite way round to shown.
They are considered to be gain their strength from acting linearly aligned to the generations of the Molimentum process, from the point of observation.
Gravity. Yes/No/Maybe
This is different since it not only requires elements of all three ingredients but is the process by which these ingredients seek to restore balance. This force is omnipotent and yet weaker than the others. It is spacetime. The other forces are only temporary, incomplete and imbalanced occurrences in spacetime.
Gravity, which I think of as an omnidirectional force, is not comparable to the quantum forces, but is the process by spacetime and all energy and matter is derived. It is the whole process from which space-time and energy-matter emerges. The process is a physical representation of time and the relational interconnection of structure and content. Basically Gravity should probably be in the structure section of this work.
It may be useful to consider each energy in terms of the absence of one part, rather than the presence of two core ingredients. I.e. Electro-magnetism is created by the absence of maybe, strong radiation is the absence of no, and weak radiation is the absence of yes. The strength of the forces comes from imbalance (with potential and an inclination to balance again) but Gravity’s force is the difference as it alone can generate the spacetime dimensions.
2.2 Matter
In this section we look to align the patterns found in Molimentum to known particles.
Standard Model
The Standard Model can be understood as having 6 items under three different sections. This process explored here shows how the Standard Model could be derived by considering them the 6 deeper states, as seen from, or multiplied by, each of the three emergent directions of separated Y, N, M.
Matter includes longitudinal items (fermions) and lateral ones (bosons).

Table 1.
This explanation considers the mass arbitrary and not important, however in the case of quarks and leptons charge and spin should align.
Quarks
This is considered to be the 6, as perceived from the Y path. The charge of these is in thirds (plus ⅔ or -⅓), so considered from a view referencing all of YNM, as split three ways.

Table 2.
It appears that quarks are a longitudinal to the Molimentum process observations of matter which reference three elemental features in their cycle. The patterns producing quark observations as thought to be running are up and down through the generations of Molimentum, like relationships between grandchildren-parents-grandparents and observed as a three way, ‘trinary’ view.
Note how this is displayed horizontally to highlight the three way split being dominant over the two way split.
Leptions
These also appear in 6 types. The charge of these are either nil or minus one. This is the result of a binary choice so only YN, and not M.

Table 3.
These appear to be longitudinal observations of matter in which the cycle references only two of the three basic elements.
Note how this is displayed vertically to highlight the binary split being dominant over the three way split.
The patterns producing lepton observations are thought to be linear, also running along the generations of Molimentum but taking a limited, binary view.

Fig 16.
Bosons
This is considered to be the 6 pairs, as perceived from the M path. These ones behave differently. Instead of neat pairs the, the bosons follow a different balance. Bosuns are about absences. This is the source of their power.
Bosons differ from fermions (quarks and leptons) in that the pattern influencing them is from running perpendicular, laterally across the Molimentum process generations (rather than along the direction of the Molimentum process).
1 Photon
The purest form of maybe. This represents a temporary absence of maybe, an enduring bouncing between yes and no.
3 Weak Bosons
(W-, Zo, W+)
These represent that there are essentially 3 ways to undo the knot of YNM. Removal of any one of the 3 elements creates an imbalance by which energy may be passed.
8 Gluons
These represent the constructive process between matter. These are essentially all the process of 3 x 3 -1. That’s the original YNM x -(MNY) and minus the original. After taking the 2 generations 3×3.
The above (photon, weak bosons, gluons) should be considered lateral bosons which relate to energy and the higgs boson should be considered a longitudinal boson which relates to matter.
1 Higgs Boson
Representing the -YNM from the YNM reflecting in itself, deviations from which are witnessed as mass. This is in effect a kind of average against which the cycle of other patterns may be witnessed. This is a longitudinal boson. It represents the average from which other patterns derive meaningful qualities.
NB.
There is no Graviton. Gravity does not act through particles as it is spacetime instead.

Fig 17.
The Periodic Table
‘Everyone knows that 8 divided by 2 is 4.
Not so many consider that 8 divided by 2 is 4, and another 4.’
As mentioned, I prefer to explore the achievement of science to generate a picture of the Universe using the fewest items, not the extremities of scales. The periodic table is the pinnacle of this middle ground. For 35yrs I’ve wondered why it’s that strange pattern? Recently I have considered that it may be visualised in a misleading way which impedes comprehension.
An Amendment
The first line shows one shell with a capacity for 2 electrons. However the system remains valid if it is redrawn as being two initial shells, each with capacity for one electron.

Fig 18.
Taking this visual starting point reveals a pattern or formula for explaining why the Periodic Table is as it is.
We take each number from 1 to 4, doubled it, then square it to the generation of the process, then split into 2 parts.
This show a by now familiar pattern, the self-reflection (of YNM within 4 dimensions).
1 doubled x square 1 generation , split = 1,1
2 doubled x square2 generation, split = 8, 8
3 doubled x square 2 generation, split= 18, 18
4 doubled x square 2 generation, split = 32, 32
It’s only 4 rows because that’s the number of dimensions.
Rows are in pairs because from the central M path there may be considered two alternatives. In fact from any one path, there are always two others.
2.3 Related Theories
Special Relativity
E=MC2
Energy = Mass x Speed of Light 2

Fig 19.
Mass = Y/N x area of spacetime
Energy = Maybe
Time = Period deviations from a standard.
Makes sense in terms of Maybe = potential = energy.
Speed of light (relative to what?) is limited to the speed of change, indicated by flipping between yes and no possible which occurs between generations.
M = Y+N x (YNM x -YNM)
General Relativity

8 is from the two generations (3×3=9) minus the 1st generation (1)
Pi is actually 22/7 which shows 22 outcomes occurring from 7 basic states.
c4 is the process spread across 4 dimensions at the speed of light.
Quantum Wave Mechanics (Schrodinger Equation)

Fig 20.
Frequency of the wave relates to the oscillation between Y, N, M.

Quantum Field Theory (Feynman Diagrams)
Fig 21.
One particle may change into another one over time.
2.4 Content Summary
In terms of content we see many similar patterns, albeit from different views. Primarily we’ve seen the division between looking laterally across the flow of the Molimentum process versus longitudinally along it. Also, it’s different depending whether the observation include all or some of the basic parts of the universe.
‘It’s only by lack of synchronicity that we may experience and comprehend our world’.
Scientific discovery depends on observations, however when looking at the smallest scale the impact of looking is tricky to remove from the equations. We need to qualify what observation is and is not in order to stand a better chance of mitigating the act of looking from results.
In summary, observation does not change observations, as many state. It’s not the observing. However, it is the synchronicity which is achieved by observing generates.
3.1 Nowness
Insight:
Swap the word quantum for the word future and it all makes more sense.
The future is small. A world of probability, uncertainty, entangled outcomes. I’ve never seen this explanation but isn’t this intuitively aligned with an sense of the conditions of a future state?
Not Now,Not There
Reading Carlo Rovelli I learnt that it doesn’t make sense to ask what time it is one moon now. There’s no common time everywhere. However, building on this, I understand that the range of the difference in time is relative to the distance between places, a range that I call ‘nowness’. I.e. the range of nowness between the sides of a cup is different to the nowness between planets. The cup examples has relatively higher nowness than the planets example.
The strength of considering nowness is that it incorporates space and time under one unit based which acknowledges their connectedness in a way which is more comprehensive than the common practice of artificially splitting them. The difference in nowness reflects an aspect of gravity as the relative mass-volume of objects and the distance between the objects are also the relevant qualities in this case.
Relative Nowness
The next extension is to consider two systems of different levels of nowness. This is the same as saying systems of different scale. This time implication of observation between different scales doesn’t appear in popular science books. I’m proposing that looking from smaller to larger we see the relative past, which is widely understood, but also that looking from bigger scales to smaller ones offers a view of the relative future.
This seems like a time equivalent of the ‘depth of field’ concept commonly found in photography.
3.2 Duality
We can consider that only 2 moments are measurable at once and the change between can be established or two changes with one moment between. Seeing the two generations shows a period of spacetime, so the change is the focus between the two bookends. The other way around, a moment in spacetime is the focus, bookended between two periods of change.

Fig 22.
Particles may be observed when there are temporarily boundaries between what is and what is not. This is energy as matter, as show below on the left and more common when systems are reduced to binary systems, e.g. when taking a snapshot in time. Waves on the other hand represent matter as energy, trapped in cycles that are dynamic. Recurring patterns represent stable energy while irregular ones represent unstable energy.

Fig 23.
In the wave view the M is the only observable as neither Y nor N are actually achieved completely. An analogy that may help (and may not) is to consider the particle view as how a video would view a photo and the wave view of how a photo would view a video.
In the particle view only the Yes and No views are observed. The M is denied.
These are the only balanced states and only balanced states are observable.
Aligning the process with particles and waves. Where situations are presented as binary (the maybe being suppressed momentarily) and only yes or no are possible answers then matter appears to be particle like. Where situations are not binary, the maybe aspect is dominant.
In conditions that negate the Maybe option particles are observed. In those that permit the Maybe option waves are observed.
A suitable analogy is money which in management accounting terms can be considered either as cashflow (moving) or as profit and loss (a moment in time). The maybe element indicates an open, dynamic view which is seen as a wave. When the maybe element is suppressed by the situation the result is a binary yes/no which can only be accurate for a moment frozen in time.
3.3 Relevant Experiments
The Bloody Cat
The false assumption is that there is actually a 50/50 binary possibility. It’s a case of a false binary situation. In fact you can’t exclude the M option entirely from a scenario.
Put another way, extrapolating a result for a larger than observer system from a smaller that observer system is problematic because as we have seen there is no simultaneity possible between objects of different sizes, relative to an observer.
It’s correct only to say the cat will die or the cat will survive based on small scale info.
Young’s Slits
This conundrum is another case of a false binary situation. Here the set up for the experiment is either for binary or non binary systems. Where a binary system is created only particles may be experienced, since they are (temporary) binary representations. Where a non-binary system (allowing the result to be M) is created the wave aspect is represented.
E.g. With two unobserved slits there is still uncertainty between each slit. With just one or with one (or two but where one is observed) there is no uncertainty within the experiment design.
3.4 Observation Summary
Relative asynchronicty is the key principle by which the universe may be observed and understood. It occurs through differences in both time and scales. With this view of observation the weirdness of quantum scenarios becomes intuitive and the gulf between quantum and relativity may be overcome.
‘The magician’s greatest trick is to convince us that the box was empty to begin with.’ [David Glen Gold]
4.1 Thinking
Insight: What if the answer is a question?
We look around and think ‘it is’ but perhaps the Universe is also asking ‘is it?’. At a basic level reasoning may be considered a threshold of basic consciousness. A question is considered to be asking yes/no/maybe about something. The Molimentum process outlines simply reflects the asking of a question. In particular, self reflection is a pattern in the process, where a question is reflected on itself. And isn;’t consciousness the ability not just to ask a question, which can be done by chance, but the awareness to know that a mind is asking a question which distinguishes a higher level of consciousness.
In terms of memories, the Molimentum process can feature echoes, in which repeating cycles could remain accessible.
4.2 Actions
It is generally understood that there’s a ‘hard problem’ whereby physical things and non physical things may not interact. Yet it appears that our minds (non physical) and our bodies (physical) do interact.)
The assumption here is that before an action there is nothing happening. That only a thought may trigger a movement, or that only a physical sensation may trigger a thought. However, there is another way to perceive things if we assume that it is in fact impossible for a body to do nothing. It is not devoid if energy and the question is not so much if it will do something but what it will do.
Our senses routinely invert signals, in particular the eyes. Colours are not the result of seeing a colour but are identified actually as the absence of certain colours from a whole spectrum. (And the images are received inverted before the brain flips them to make better sense). Could it be that our actions are not actually first choice, direct actions as decided by the mind, but last result after division of options and the final inaction is interpreted by us as a manifestation of an action. An inaction (non physical) could relate to other non physical things (like a mind).
As such, our thinking would be less like constructively building a sandcastle on the beach by adding and more like digging a hole into which some things are more likely to fall in than others. There would be less control that a free will with direct mind to body linkage, but enough consistency from what falls into the hole to give the impression of free will.
This logically aligns with the view that mediation, the practice of stilling the mind, is associated with higher levels of consciousness. In some sense the ability for a mind to control a body is not so much about control but a sense of building the conditions for an absence of control. This aligns with the absence of friction in flow states.
As for how impact on the body (e.g. pain ) results in thoughts, it is possible that the last inaction theory view is played in reverse and… [this is really hard to explain!] It is possible that of all the possible narratives in response to a physical actions, the non physical thoughts mimic the division down to last inaction and result in a last standing thought. This works on the same basis that just like the body never being fully still, neither is the mind fully still, so there is always something that changes, rather than a need to get something from nothing.
Another analogy that might be helpful is the lighthouse. Mostly we think of a lighthouse as flashing periodically, perhaps with 3 flashes of light every 10 seconds. What is being suggested here is what is called ‘occulting’ in navigation terms, whereby the lighthouse is always on, with the exception of it going off 3 times every 10 seconds, but with an interruption that appears as a flash of darkness. Notably the dark flash has meaning and yet there is physical thing. The meaning comes from the absence or difference to the default.
Crucially, the Molimentum process also displays a process whereby there is a reduction as energy is left over and seeks to find form by a similar reductive process which indicates how one process can account for the processes required to support not just the structure and content of the Universe but also the observation and consciousness required to comprehend this.
Physical things (like brains) reconfigure themselves owing to a quality called plasticity. This is accounted for by the same process Wheeler identified for the cosmos, that spacetime tells matter how to move and matter tells spacetime how to bend. The default setting of our brains can and does change as the life plays out and the interplay between mind and body lead to evolving default states.
Plasticy
Owing to plasticity the shape of a brain changes. This creates gaps/overlaps between the past brain and the future brain. The changes include changes to non physical spaces (gaps) from thought processes. It’s as if the software is impacting the shape of the hardware, and the hardware is shaping the software.
Processes running through hardware can change the hardware over time. This is an example of non physical processes impacting physical processes.

Fig 24.
As change occurs, there becomes an area which is no longer part of the system. This ‘no longer’ part may have an impact on the rest of the system but is itself non physical.
4.3 Subconsciousness
Now this stuff is really speculative. If you thought the earlier information was too vague for you, you really won’t like this section! It’s what would be considered in the Rumsfeld Matrix, the unknown knowns.
However, it’s fun to look at ways in which patterns evident in the Molimentum process are naturally and unwittingly come to represent aspects of humanity.
Throwaway Lines
‘Quantum is algebra and relativity is geometry’.
Brains
Two hemispheres, one reductive and one constructive, plus the corpus callosum.
Short Term (Reptilian) Dominated by rapid, binary, Yes/No thinking.
Long Term (Mammalian) Dominated by slow, consideration, evocative of thinking maybe.
Blending the two is the role of a third part, the corpus callosum.
Expressions
‘The only constant is change’.
Sleep
Our sleeping hours are usually one third of the 24hr day. During these 8 hours we dream and it could be that this represents the Maybe element as opposed to the day time when we’re in a world of logic, options, and Yes/No decisions dominate.
Religious/Spiritual Symbols.
Is it possible that religious movements have become branded with logos that be seen as inadvertently but perhaps intuitively resonate with the process described.
The Christian cross can be seen as one lines splitting into three lines, reflecting how the process splits three ways between generations.
The Jewish star shows two triangles overlayed. Like the three points of YNM x another YNM.
The Islamic crescent is reminiscent of two circular shapes overlapping and showing the inverted nature of one being solid and the other transparent.
Druidism – The Triskelion is significantly symmetrical three ways, matching the importance of threes to the Molimentum patterns.
Buddhism – The Wheel of Dharma infers a cyclical nature, as well as the 4 fold image aligning with the four corners of the tetrahedron which is the geometric form of Molimentum.

Fig 25.
From my shakti mat. Illustrative of 4 dimensions and multiplying triangles.
Hinduism – Om. Three parts. When taken letter by letter, A-U-M represents the divine energy (shakti) united in its three elementary aspects: Brahma Shakti (creation), Vishnu Shakti (preservation) and Shiva Shakti (liberation, and/or destruction). These are similar to the three lateral (quantum) forces.
Taoism – Yin and Yang shows opposing content with the M element represented by the dots inside the main shapes.
National Symbols
It’s very common for flags to feature trios.

Genetics
GTCA, mimics the dual dualism. In this case, -Y is considered different to N, and -N is different to Y.
Also, in terms of chromosomes, the XY of males is indicative of the masculine characteristic of blunt, Yes/No decision making while the XX of females is indicative of more subtle consideration.
Life
The process of things coming together and breeding before dying is strikingly similar to the process of Molimentum which ultimately provides a fertile and recurring pattern for creation, interactions, and decomposition.
And Douglas Adams…
Famously Douglas Adams proclaimed the answer to the Universe being 42. This can be generated by 7×7-7. This aligns somewhat with the process we’ve explored, in which the original thing is multiplied by itself, before then subtracting the original from the result of the multiplication.
4.4 Consciousness Summary
We’ve seen the processes of reflection, leftovers, cycles and balance that appear represented in the physical world appear also inside our minds, both consciously and subconsciously.
5.0 Conclusion
1- Summary
In summary, by equating the relatively small as a form of relative future we can unlock the confusion surrounding unifying the quantum and classical observations of the world. In unfurling this work further, the main headlines are that the Molimetum process is Gravity. Dark Matter is macro-Gravity-past. Dark Energy is micro-Gravity-future’. Spacetime is emergent from the Molimentum process. Molimentum is Gravity. NB, I’m giving Gravity a capital letter to indicate its elevated importance as understood according to Molimentum Theory.
The quantum forces of electro-magnetism, weak radiation and strong radiation are linear forces recurring along the generational flow of the Molimentum process and matter is the effect of lateral, perpendicular to the the flow of the process.
2- Testing
- Scales. Studying the impact of different scale comparisons between observer and observed ought to reveal relative degrees of time differences.
- Fulcrum. The Higgs appears to provide a baseline unit, from which not just matter derives mass but also from which bosons may derive mass and matter may derive energy.
- Proportions. The distribution of physical phenomena is likely to show observable pendulum like swinging between being in and out of balance.
3- Unknowns
a) How does Molimentum impact our understanding of more.
- Multiverses.
- Big bounces
- Relational physics.
- Holograms.
- Causality.
- Free will.
- Chicken/egg problem?